Cataracts Symptoms: Cataracts, a common yet often misunderstood eye condition, affect millions globally.
This comprehensive guide delves into the symptoms and causes of cataracts, offering vital information for understanding and managing this eye condition.
What are Cataracts?
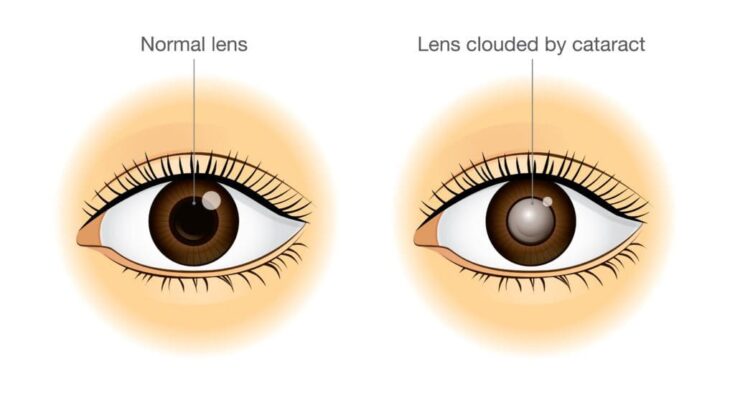
Cataracts are a common eye condition characterized by the clouding of the lens in the eye, leading to a decrease in vision. They are often associated with aging, but can also result from other factors such as genetics, medical conditions, or eye injuries. This clouding occurs when the proteins in the lens of the eye clump together, obstructing clear vision. Cataracts can develop in one or both eyes, but they do not spread from one eye to the other.
Statistics about Cataracts Prevalence
Cataracts are the leading cause of vision impairment worldwide. According to the World Health Organization, cataracts are responsible for approximately 51% of world blindness, representing about 20 million people. In the United States alone, more than 24.4 million individuals over the age of 40 are affected by cataracts. This number is projected to grow to over 38 million by 2030. The prevalence of cataracts increases dramatically with age. For instance, by the age of 80, more than half of all Americans either have a cataract or have undergone cataract surgery.
Different Types of Cataracts
- Nuclear Cataracts: These develop in the central zone (nucleus) of the lens. Nuclear cataracts are most commonly associated with aging.
- Cortical Cataracts: Characterized by white, wedge-like opacities that start in the periphery of the lens and work their way to the center in a spoke-like fashion. These are commonly found in people with diabetes.
- Posterior Subcapsular Cataracts: These form faster than the other types and affect the back of the lens. People with diabetes, high myopia, retinitis pigmentosa or those taking high doses of steroids may have a higher risk of developing this type of cataract.
- Congenital Cataracts: Some people are born with cataracts or develop them during childhood. These can be hereditary or associated with intrauterine infection or trauma.
Each type of cataract has different symptoms and affects vision in its unique way. However, common signs include blurring, sensitivity to light, and difficulty with night vision. Early detection and treatment are crucial for maintaining good eye health and preventing vision loss due to cataracts. Regular eye examinations are recommended, especially for those over the age of 40 or with risk factors for cataracts.
Early Symptoms of Cataracts: Recognizing the Warning Signs
Here, we will delve into the early signs of cataracts, differentiate these symptoms from other eye conditions, and share personal anecdotes or case studies to give you a clearer picture.
Detailed Description of Early Signs
Cataracts develop gradually, and in the early stages, symptoms might be mild. Here are some common early indicators:
- Blurry Vision: One of the first signs is a slight blurriness in vision, akin to looking through a foggy window.
- Glare Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to light and glare is common, often accompanied by halos around lights, particularly noticeable at night.
- Faded Colors: Colors may appear less vibrant, and vision might start having a yellowish or brownish tinge.
- Difficulty with Night Vision: As cataracts progress, you may find it harder to see in low-light conditions.
- Frequent Prescription Changes: A noticeable and frequent change in eye prescription can be an early warning sign.
How Cataracts Symptoms Differ from Other Eye Conditions
Distinguishing cataract symptoms from other eye conditions is crucial for appropriate treatment:
- Cataracts vs. Glaucoma: Unlike glaucoma, which can cause peripheral vision loss, cataracts primarily affect the center of your vision.
- Cataracts vs. Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD): AMD affects the macula and leads to a loss in central vision, while cataracts cause overall blurring and decreased color perception.
- Cataracts vs. Diabetic Retinopathy: Diabetic retinopathy often results in floating spots or streaks in vision, which is not a typical symptom of cataracts.
Personal Anecdotes or Case Studies
While clinical symptoms are helpful, personal stories can provide a deeper understanding:
- Case Study 1: A 65-year-old patient initially complained of difficulty driving at night due to glaring headlights. An eye examination revealed early-stage cataracts.
- Personal Anecdote: Sarah, a graphic designer, noticed that colors seemed less vibrant and her vision was slightly blurry. Initially attributing it to aging, a visit to the ophthalmologist confirmed early cataracts.
Understanding the early symptoms of cataracts and knowing how they differ from other eye conditions can lead to quicker diagnosis and treatment. Regular eye examinations are vital, especially as you age, to catch these symptoms early. If you notice any changes in your vision, consult with an eye care professional for a thorough evaluation.
Progression of Cataracts Symptoms
Understanding the progression of cataracts symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective management. In this section, we will delve into how cataract symptoms evolve, the visual changes individuals may experience, and the impact on daily life and activities.
Evolution of Cataract Symptoms Over Time
Cataracts typically develop gradually, and early symptoms can be so subtle that you might not even notice them. Initially, you may experience a slight blurring of vision, akin to looking through a cloudy lens. As the cataract progresses, this cloudiness intensifies, leading to more noticeable vision impairment.
Stages of Symptom Progression:
- Early Stage: Minor blurring, slight difficulty with vision at night, and a mild sensitivity to light.
- Intermediate Stage: Increased blurriness and difficulty in distinguishing colors. Glasses prescriptions may change frequently.
- Advanced Stage: Vision becomes significantly impaired, making daily activities challenging. This can include a noticeable decrease in color intensity and contrast sensitivity.
Visual Changes Experienced by Individuals
The experience of cataract progression can vary, but common visual changes include:
- Blurred or Dim Vision: The most common symptom, where vision gradually becomes foggy or unfocused.
- Glare Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to light and glare, especially at night, which can cause problems while driving.
- Halos Around Lights: Rings or halos may appear around lights, further complicating night vision.
- Yellowing of Vision: Over time, the lens may turn yellowish, altering color perception.
- Frequent Prescription Changes: A notable sign of cataracts is the need to frequently update eyeglass or contact lens prescriptions.
Impact on Daily Life and Activities
The progression of cataract symptoms can profoundly affect daily activities:
- Reading and Writing: Blurred vision can make it difficult to read print or see details.
- Driving: Impaired night vision and sensitivity to glare can make driving hazardous, particularly at night.
- Recognizing Faces: Difficulty in seeing fine details can make it hard to recognize faces, impacting social interactions.
- Hobbies: Activities that require sharp vision, like sewing or painting, become more challenging.
However, the progression of cataract symptoms involves a gradual worsening of vision quality, impacting various aspects of daily life. Early detection and treatment are key to managing this condition effectively. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is advisable to consult an eye care professional for a comprehensive eye examination. Remember, managing cataracts effectively starts with understanding their progression and seeking timely care.
Causes of Cataracts: Understanding Risks and Prevention
Understanding the causes of cataracts is crucial for both prevention and treatment. This article offers an in-depth exploration of the various causes of cataracts, delineating between preventable and non-preventable factors.
In-Depth Exploration of Various Causes
Cataracts can develop due to a range of reasons, often linked to aging. However, other factors also play a significant role:
- Aging: The most common cause, with the risk increasing as you age.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of cataracts can increase your risk.
- Medical Conditions: Diseases like diabetes significantly heighten the risk.
- Eye Injuries or Surgeries: Past injuries or surgeries can lead to cataract development.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute.
- Prolonged Exposure to Sunlight: UV rays can damage the lens, leading to cataracts.
- Certain Medications: Long-term use of corticosteroids and other medications can be a contributing factor.
Risk Factors Contributing to Cataract Development
Identifying risk factors is key in cataract prevention. Here are some significant ones:
- Age: Individuals over 60 are at a higher risk.
- Diabetes: Diabetics are more likely to develop cataracts at a younger age.
- Unhealthy Habits: Smoking and excessive alcohol use can accelerate cataract formation.
- Exposure to Sunlight: Without adequate eye protection, UV light exposure can increase the risk.
- Obesity: Higher body mass index (BMI) has been linked to increased cataract risk.
Discussion on Preventable vs. Non-Preventable Causes
While some causes, like aging and genetics, are non-preventable, many lifestyle-related factors are within your control:
Preventable Causes:
- Wear sunglasses to protect against UV rays.
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in antioxidants.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
- Manage health conditions like diabetes effectively.
Non-Preventable Causes:
- Aging is inevitable and the most common cause of cataracts.
- Genetic predisposition is beyond one’s control.
Understanding these factors is vital in taking proactive steps towards eye health. Regular eye examinations, especially as you age or if you have risk factors, can help in early detection and treatment of cataracts.
However, while certain causes of cataracts are unavoidable, understanding and managing risk factors can play a pivotal role in prevention and maintaining good eye health. Stay informed and proactive in your approach to reduce the risk of cataracts.
Diagnosing Cataracts: A Comprehensive Guide
The process of diagnosing cataracts is critical for ensuring timely and effective treatment. Cataracts, a common eye condition where the lens becomes clouded, can significantly impair vision if left untreated. The diagnostic process involves several steps, each aimed at confirming the presence of cataracts and assessing the extent of vision impairment.
- Initial Eye Examination: The process typically begins with a comprehensive eye examination. An eye care professional will review your medical history and symptoms. This step is crucial for understanding any factors that may contribute to cataract development, such as age, medical conditions, or a history of eye injuries.
- Visual Acuity Test: This test involves reading an eye chart, which helps determine how well you can see at various distances. It’s a fundamental part of the diagnostic process and helps in assessing the impact of cataracts on your vision.
- Slit-lamp Examination: The slit-lamp, a microscope with a bright light, allows the doctor to examine the structures at the front of your eye under magnification. This examination is key in identifying cataracts and other eye conditions.
- Retinal Examination: After dilating your pupils, the eye care professional examines the retina and the lens for signs of cataract. This step is vital for a thorough evaluation of your eye health.
- Tonometry: This test measures the pressure inside your eye, which is important for ruling out other eye conditions like glaucoma.
Types of Tests and Examinations Used
- Visual Acuity Test: As mentioned, it assesses how well you can see at different distances.
- Slit-lamp Examination: Provides a magnified view of the eye’s structures, detecting cataracts and other issues.
- Retinal Examination: Essential for a full assessment of the lens and the back of the eye.
- Tonometry: Helps identify other possible eye problems by measuring internal eye pressure.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of cataracts is crucial. It not only helps in slowing down the progression of the condition but also opens up more treatment options. Early-stage cataracts might be managed with new prescription glasses, brighter lighting, or anti-glare sunglasses. However, as cataracts progress, they can severely impair vision, leading to a significant decrease in quality of life. Timely diagnosis allows for early intervention, which can lead to better management of the condition and a higher likelihood of successful treatment outcomes.
However, the process of diagnosing cataracts involves a combination of eye examinations and tests, each playing a pivotal role in detecting and assessing the severity of the condition. Understanding the importance of early detection can encourage individuals to seek prompt medical attention, leading to more effective management of cataracts.
Treatment Options for Cataracts
Understanding the available treatment options is crucial for those affected. This article explores non-surgical approaches, surgical treatments, and recent advancements in cataract treatment, providing a comprehensive guide for those seeking relief from this condition.
Non-Surgical Approaches to Cataract Treatment
While surgery is the most definitive treatment for cataracts, there are non-surgical options that can help manage symptoms in the early stages:
- Stronger Eyeglasses or Magnifying Lenses: Prescription changes in eyeglasses or the use of magnifying lenses can sometimes compensate for the loss of clear vision, albeit temporarily.
- Anti-Glare Sunglasses: These can reduce glare and sensitivity to light, common symptoms associated with cataracts.
- Adjusting Lighting Conditions: Enhancing lighting at home or work can help alleviate some difficulties caused by reduced vision.
It’s important to note that while these methods can offer temporary relief, they do not halt the progression of cataracts. Regular eye examinations are crucial for monitoring the condition.
Surgical Treatments and Their Effectiveness
Surgery is the most effective treatment for cataracts, with a high success rate. The two primary surgical options are:
- Phacoemulsification (Phaco): This is the most common technique where a small incision is made in the eye to insert an ultrasonic probe. The probe breaks up the cloudy lens, which is then suctioned out. A clear artificial lens is implanted in its place.
- Extracapsular Cataract Extraction (ECCE): Used for advanced cataracts, this procedure involves a larger incision to remove the cloudy lens in one piece. As in Phaco, an artificial lens is implanted.
Both procedures are typically done on an outpatient basis, with local anesthesia, and have a recovery time of a few weeks. The success rate of cataract surgery is high, with most patients experiencing a significant improvement in vision.
Recent Advancements in Cataract Treatment
The field of cataract treatment is constantly evolving, with recent advancements aimed at improving outcomes and recovery times:
- Laser-Assisted Cataract Surgery: Utilizing femtosecond lasers, this advanced technique offers precision in lens removal and incision creation, potentially reducing risks and improving recovery times.
- Advanced Intraocular Lenses (IOLs): New designs in IOLs, such as multifocal and accommodative lenses, aim to enhance vision quality post-surgery, sometimes reducing the need for glasses.
- Minimal Incision Surgery: Techniques are being developed to minimize incision sizes further, promoting faster healing and reducing infection risks.
These advancements demonstrate the ongoing commitment to improving cataract treatment, offering hope for better vision and quality of life for those affected.
However, while non-surgical methods can provide temporary relief in the early stages of cataracts, surgery remains the most effective treatment. With high success rates and continual advancements in technology, cataract surgery offers a promising solution for those seeking to restore their vision. Regular consultations with an eye care professional are essential for determining the best course of action based on individual needs.
Prevention and Management of Cataracts
Cataracts, a common eye condition characterized by the clouding of the eye’s natural lens, can significantly impact vision. Although age-related factors primarily influence cataract development, certain measures can help in slowing down their progression:
- Protect Your Eyes from Ultraviolet Light: Wearing sunglasses that block 100% of UVA and UVB rays can shield your eyes from the harmful effects of the sun, which is known to accelerate cataract development.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for cataracts. Quitting smoking can reduce the risk of cataract formation and improve overall eye health.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption is linked to an increased risk of cataracts. Moderation is key for eye health.
- Manage Health Conditions: Chronic diseases like diabetes can increase the risk of cataracts. Proper management of such conditions through medication and lifestyle choices is essential.
- Avoid Steroid Use: Long-term use of steroids can increase the risk of cataract development. If steroids are medically necessary, discuss the risks with your doctor.
Lifestyle and Dietary Recommendations
A healthy lifestyle can play a significant role in preventing cataracts. Incorporating the following habits and dietary choices can be beneficial:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: A diet rich in antioxidants (found in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains) can help protect your eyes. Vitamins C and E are particularly important for eye health.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate water intake is essential for maintaining the health of your eyes.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity can reduce the risk of cataracts by improving overall health and blood circulation.
- Control Blood Sugar Levels: High blood sugar can affect the lenses of your eyes, increasing the risk of cataracts.
Regular Eye Examinations and Care
Regular eye exams are crucial in detecting cataracts at an early stage and managing their progression:
- Routine Eye Check-Ups: Adults should have comprehensive eye exams at least once every two years. Those over 60 or with a history of eye problems may need more frequent check-ups.
- Follow the Doctor’s Advice: If cataracts are detected, it’s important to follow your doctor’s recommendations, which may include lifestyle changes or planning for cataract surgery.
- Monitor Vision Changes: Any significant changes in vision should be reported to an eye care professional immediately.
- Use Corrective Eyewear: Properly prescribed glasses or contact lenses can help manage the symptoms of cataracts and improve vision.
By adopting these preventive measures and management strategies, you can play an active role in maintaining your eye health and potentially slowing the progression of cataracts. Remember, early detection and lifestyle modifications are key components in the effective management of this condition.
Living with Cataracts
Living with cataracts can be challenging, but making certain adjustments and accommodations in your daily life can significantly improve your quality of life. Here are some practical tips:
- Enhance Lighting: Increase the amount of light in your home. Use brighter bulbs and consider task lighting in areas where you perform detailed work.
- Use High-Contrast Colors: High contrast between objects and their backgrounds can make it easier to see. For example, use a dark cutting board for light-colored vegetables.
- Magnify: Reading glasses or magnifying glasses can be helpful for reading and detailed tasks.
- Reduce Glare: Wear sunglasses or a wide-brimmed hat outdoors. Indoors, use blinds or shades to reduce glare from windows.
- Organize and Label: Keep your home well-organized and label items with large, bold print to find them easily.
- Safety First: Install handrails and non-slip mats in potentially hazardous areas like bathrooms.
Support and Resources Available
Having a support system and knowing where to find resources is crucial in managing life with cataracts. Consider the following:
- Healthcare Professionals: Regular check-ups with an eye doctor are essential. They can provide medical advice and keep you updated on your condition.
- Support Groups: Joining a support group can connect you with others who understand your experiences. It’s a great way to share tips and feel less isolated.
- Educational Material: Look for brochures, books, and online resources specifically designed for individuals with cataracts.
- Vision Aid Organizations: Organizations such as the American Foundation for the Blind offer resources and assistance for those with vision impairments.
- Technology Aids: Explore apps and devices designed for visual impairment. These can range from text-to-speech applications to specialized computer software.
Patient Perspectives and Coping Strategies
Hearing from others who are also living with cataracts can provide comfort and practical advice. Here are some common coping strategies:
- Stay Positive: Focusing on what you can do, rather than what you can’t, helps in maintaining a positive outlook.
- Adapt and Learn: Be open to learning new ways to do things and adapting to your changing vision.
- Communicate Your Needs: Don’t hesitate to let friends, family, and colleagues know about your vision limitations and how they can help.
- Stay Active: Engage in activities that are safe for your level of vision. Physical exercise and social interactions are important for overall well-being.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation: Practices like meditation and deep breathing can help in dealing with stress and anxiety related to vision loss.
Living with cataracts requires adjustments, but with the right strategies and support, you can continue to lead a fulfilling life. Remember, you are not alone in this journey.
FAQs about Cataract Symptoms
1. What are the first signs of cataracts?
Early cataract symptoms include blurry vision, increased sensitivity to light, and difficulty seeing at night. You may also notice colors appearing faded or a halo around lights.
2. Can cataracts cause sudden vision loss?
No, cataracts usually develop gradually. Sudden vision loss is rare and may indicate another serious eye condition that requires immediate medical attention.
3. Do cataracts cause pain or redness?
Cataracts do not typically cause pain, redness, or eye discharge. If you experience these symptoms, consult an eye doctor promptly as they may signal other eye issues.
4. Are cataracts only age-related?
While most cataracts are age-related, they can also develop due to diabetes, eye injuries, certain medications (like steroids), or as a congenital condition at birth.
5. Can cataracts affect just one eye?
Yes, cataracts can affect one eye, though they often develop in both eyes over time. However, the severity may differ between each eye.
6. How do I know if I have cataracts or just need new glasses?
If changing your glasses doesn’t improve blurry vision, and you struggle with glare, halos, or night driving, a cataract exam by an ophthalmologist is recommended.
Conclusion
We encourage our readers to prioritize their eye health. Regular check-ups, protecting eyes from excessive sunlight, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and being aware of changes in vision are key steps in preventing and managing cataracts. If you notice any symptoms or changes in your vision, do not hesitate to consult with an eye care professional.
Remember, taking care of your eyes today can lead to a clearer, brighter future. Don’t let cataracts cloud your vision and your life. Stay informed, stay proactive, and ensure your eyes receive the care they deserve.