Castleman Disease Treatment: Castleman Disease, a rare and complex lymphoproliferative disorder, presents unique challenges in both its diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding the intricacies of this disease is crucial for providing optimal patient care.
What is Castleman Disease?
Castleman disease is a rare and complex condition that affects the lymph nodes and related tissues. It is a disorder characterized by an overgrowth of cells in the body’s lymphatic system. This growth can lead to a range of symptoms, depending on the type and severity of the disease. Understanding Castleman disease involves looking at its epidemiology, including its prevalence and demographics, and differentiating between its two main types: unicentric and multicentric.
Epidemiology: Prevalence and Demographics
Castleman disease is considered a rare condition, with a relatively low prevalence rate worldwide. However, exact numbers are hard to determine due to the rarity and complexity of the disease. It can occur in individuals of any age, but certain types are more common in specific age groups. For example, the unicentric type is often diagnosed in younger adults, while the multicentric type tends to occur in older individuals. There is no significant gender bias in the prevalence of Castleman disease, and it has been reported in various ethnic and racial groups, indicating a broad demographic impact.
Types of Castleman Disease: Unicentric and Multicentric
Castleman disease is primarily categorized into two types: unicentric and multicentric.
- Unicentric Castleman Disease (UCD): This type is localized, affecting only one lymph node region or a single group of nodes. Symptoms are usually less severe, and the disease often goes unnoticed or is found incidentally during investigations for other conditions. UCD is typically treatable with surgery, and the prognosis is generally favorable.
- Multicentric Castleman Disease (MCD): MCD is a more aggressive form that involves multiple lymph node regions. It can also affect lymphoid tissue of internal organs. MCD is associated with systemic symptoms like fever, weight loss, and fatigue. Treatment for MCD is more complex and can include medications to regulate the immune system. The prognosis for MCD can vary and is often dependent on the underlying cause and the individual’s overall health.
However, Castleman disease, while rare, is a significant medical condition with varying manifestations and outcomes. Understanding its epidemiology and the differences between its types is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Symptoms and Early Detection of Castleman Disease
Castleman Disease, a rare disorder that affects the lymph nodes and related tissues, is often challenging to diagnose due to its uncommon nature and varied symptoms. Understanding the common symptoms and the crucial role of early detection can significantly impact the effectiveness of treatment.
Common Symptoms of Castleman Disease
Castleman Disease presents a range of symptoms, many of which are similar to those of other illnesses, making it difficult to diagnose. Key symptoms include:
- Enlarged Lymph Nodes: The most common symptom, these enlarged nodes can be felt in the neck, collarbone region, underarms, or groin.
- Unexplained Fatigue: A significant drop in energy levels without a clear cause.
- Fever and Night Sweats: Recurring fevers and sweating during sleep.
- Unintentional Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying, which is often rapid and significant.
- Weakness and Shortness of Breath: Difficulty in performing regular activities due to weakness and breathlessness.
- Skin Rashes: Unexplained skin changes or rashes.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be indicative of other conditions, and having one or more of them does not necessarily mean a person has Castleman Disease.
The Role of Early Detection in Effective Treatment
Early detection plays a pivotal role in the effective management and treatment of Castleman Disease. When diagnosed early, treatment options are more likely to be successful, and the risk of complications is reduced. Early detection can:
- Facilitate Timely Treatment: Prompt diagnosis allows for early intervention, which can prevent the disease from advancing.
- Improve Treatment Outcomes: Early-stage Castleman Disease often responds better to treatments like medications, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy.
- Reduce Risk of Complications: Early detection and treatment can help prevent complications such as organ damage or failure.
- Enhance Quality of Life: Early management of the disease can maintain a better quality of life and reduce symptoms.
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above or have concerns about Castleman Disease, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional. They can conduct necessary tests and provide appropriate guidance. Remember, while Castleman Disease is rare, awareness and early detection can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes.
Diagnostic Procedures for Castleman Disease
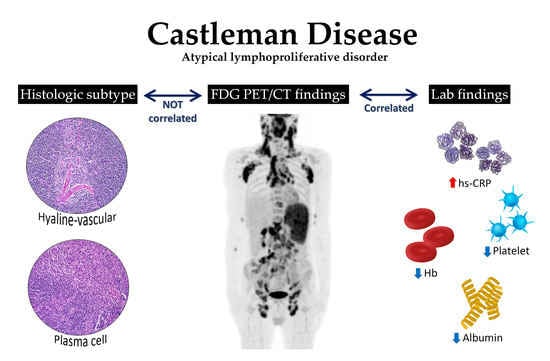
Castleman Disease, a rare lymphoproliferative disorder, requires comprehensive diagnostic procedures for accurate detection and treatment planning. Early and precise diagnosis is crucial for managing this complex condition effectively. This article delves into the primary diagnostic procedures used to identify Castleman Disease, focusing on blood tests and biomarkers, imaging techniques, and biopsy and histopathological analysis.
Blood Tests and Biomarkers
Importance of Blood Tests in Castleman Disease
Blood tests play a pivotal role in the initial screening and diagnosis of Castleman Disease. They help in assessing the overall health of the patient and in identifying abnormal levels of certain substances that may indicate the presence of the disease.
Key Blood Tests and Biomarkers
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): A CBC test measures the levels of different blood cells and can reveal abnormalities such as anemia or elevated white blood cell count.
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) and C-Reactive Protein (CRP): These tests measure inflammation in the body, which can be elevated in Castleman Disease.
- Serum Protein Electrophoresis (SPEP): This test evaluates the different proteins in the blood and can detect abnormal levels of immunoglobulins often associated with Castleman Disease.
- IL-6 Levels: Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a cytokine that plays a role in immune response and can be elevated in Castleman Disease.
Imaging Techniques
Role of Imaging in Castleman Disease
Imaging techniques are crucial in Castleman Disease diagnosis, aiding in the visualization of lymph node enlargement and other affected areas in the body.
Common Imaging Techniques Used
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: A CT scan provides detailed cross-sectional images of the body and is particularly effective in showing enlarged lymph nodes and other abnormalities.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of organs and tissues and is useful for evaluating the extent of the disease.
Biopsy and Histopathological Analysis
Biopsy: A Critical Diagnostic Step
A biopsy, the removal of a small tissue sample for examination, is often necessary to confirm a diagnosis of Castleman Disease.
Histopathological Analysis: Examining the Tissue
- Histopathology: This involves examining the biopsy tissue under a microscope. Pathologists look for characteristic features of Castleman Disease, such as specific changes in the lymph nodes.
- Immunohistochemistry: This technique involves staining the tissue with antibodies to detect specific proteins that are indicative of Castleman Disease.
However, the diagnostic process for Castleman Disease involves a combination of blood tests, imaging, and biopsy with histopathological analysis. These procedures collectively help in making an accurate diagnosis, which is essential for effective treatment and management of the disease. Patients exhibiting symptoms suggestive of Castleman Disease should consult healthcare professionals for a thorough evaluation using these diagnostic techniques.
Treatment Options for Castleman Disease
Understanding the various treatment options available is crucial for patients and caregivers. This section aims to elucidate the list of treatment approaches for CD, with a particular focus on the role of corticosteroids and antiviral therapy in Multicentric Castleman Disease (MCD).
List of Treatment Approaches for Castleman Disease
Surgical Removal: When feasible, the surgical removal of the affected lymph node(s) can be an effective treatment for Unicentric Castleman Disease (UCD).
Medications: Medications play a pivotal role in treating CD, especially MCD. These include:
- Immunomodulatory Drugs: These drugs help regulate the immune system.
- Chemotherapy: Used in certain cases to target rapidly dividing cells.
- Targeted Therapies: Such as monoclonal antibodies, specifically targeting pathways involved in CD.
Radiation Therapy: In cases where surgery isn’t viable, radiation can be used to shrink the lymph nodes.
Corticosteroids: These are anti-inflammatory drugs that can be effective in reducing symptoms and inflammation associated with MCD.
Antiviral Therapy: Particularly used in patients with HIV-associated MCD to control the underlying viral infection.
Role of Corticosteroids and Antiviral Therapy in Multicentric Castleman Disease
In Multicentric Castleman Disease, a more aggressive form of CD, corticosteroids and antiviral therapies play a significant role:
- Corticosteroids: These drugs, like prednisone, are often the first line of treatment in MCD. They work by reducing inflammation and can be quite effective in managing symptoms. However, long-term use can have significant side effects, necessitating careful management under medical supervision.
- Antiviral Therapy: For MCD associated with HIV, antiviral therapy is critical. It helps control HIV, thereby reducing the exacerbation of MCD symptoms. In patients with HHV-8 (Human Herpesvirus 8) associated MCD, antiviral therapy targeting HHV-8 can be beneficial.
However, treatment for Castleman Disease varies depending on the type (UCD or MCD) and the individual patient’s condition. Corticosteroids and antiviral therapy have a crucial role in managing MCD, particularly in cases associated with viral infections like HIV or HHV-8. It’s essential to have a multidisciplinary team approach for the effective management of this disease. Regular follow-ups and adjustments in treatment plans are necessary to ensure the best outcomes for patients suffering from Castleman Disease.
Emerging Treatments and Research in Castleman Disease: A Look at the Future
Castleman Disease, a rare and complex lymphoproliferative disorder, has seen significant strides in treatment and research. Understanding the latest advancements and ongoing clinical trials is crucial for patients, healthcare professionals, and researchers alike. This section delves into the emerging treatments and research for Castleman Disease, highlighting the progress and future prospects in this field.
Latest Advancements in Castleman Disease Treatment
Recent years have witnessed groundbreaking advancements in the treatment of Castleman Disease. These developments are not only enhancing the quality of life for patients but also paving the way for more effective management strategies. Key advancements include:
- Targeted Therapies: The introduction of targeted therapies, specifically designed to attack cancer cells without harming normal cells, has been a game-changer. These therapies focus on specific aspects of the cancer cells, such as proteins or genes that contribute to the disease’s progression.
- Immunotherapy: This innovative approach boosts the body’s immune system to fight the disease. Immunotherapies have shown promising results in treating certain types of Castleman Disease, particularly in cases where traditional treatments are less effective.
- Advances in Diagnostic Techniques: Improved diagnostic methods have led to earlier and more accurate detection of Castleman Disease. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and better patient outcomes.
- Personalized Medicine: Personalized or precision medicine is becoming increasingly important in treating Castleman Disease. This approach involves tailoring treatment based on the individual’s genetic makeup, environment, and lifestyle, leading to more effective and less toxic treatments.
Ongoing Clinical Trials and Future Prospects
The landscape of Castleman Disease treatment is evolving rapidly, thanks to ongoing clinical trials and research. These trials are exploring new treatments and combinations of existing therapies to discover the most effective approaches.
- Exploring New Drug Combinations: Clinical trials are currently investigating the efficacy of combining different drugs to enhance treatment effectiveness. These combinations might include traditional chemotherapy drugs, newer targeted therapies, or immunotherapies.
- Gene Therapy: Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment for Castleman Disease. This approach involves modifying the patient’s genes to fight the disease more effectively.
- Stem Cell Transplantation: Stem cell transplantation is another area of research that holds promise for treating Castleman Disease, especially in cases where other treatments have failed.
- Future Prospects: The future of Castleman Disease treatment looks promising, with ongoing research focusing on understanding the underlying mechanisms of the disease. This knowledge will lead to the development of more targeted and effective treatments.
However, the field of Castleman Disease treatment and research is witnessing an exciting era of innovation and discovery. As we continue to explore new treatments and refine existing ones, there is renewed hope for patients battling this rare disease. It’s essential to stay informed about the latest developments and participate in clinical trials if possible, as this contributes to the advancement of knowledge and the discovery of more effective treatments.
Managing Castleman Disease: A Multidisciplinary Approach
Importance of a Comprehensive Care Team
Castleman Disease, a complex lymphatic disorder, necessitates a multidisciplinary approach to ensure effective management. This approach involves a comprehensive care team consisting of various healthcare professionals, each playing a crucial role in the patient’s treatment journey. The team typically includes hematologists, oncologists, immunologists, and primary care physicians, who work collaboratively to develop and implement a personalized treatment plan.
The involvement of multiple specialists is pivotal in addressing the multifaceted nature of Castleman Disease. Hematologists and oncologists primarily focus on the medical management of the disease, often involving medications like immunotherapy or chemotherapy. Immunologists contribute their expertise in understanding the immune system’s involvement, essential in tailoring the treatment to individual patient needs. Meanwhile, primary care physicians play a critical role in the overall health management of the patient, ensuring that the treatment for Castleman Disease is integrated seamlessly with the management of any other existing health conditions.
Additionally, the care team may include nurses, nutritionists, physical therapists, and mental health professionals. Nurses provide essential care coordination and patient education, ensuring that treatments are administered correctly and that patients understand their medication regimens. Nutritionists can offer dietary advice to help manage symptoms and improve overall health, while physical therapists assist in maintaining physical strength and mobility, which can be affected by both the disease and its treatments. Mental health professionals address the emotional and psychological impact of living with a chronic illness, offering counseling and support to both patients and their families.
Role of Supportive Care and Lifestyle Modifications
Supportive care plays a vital role in managing Castleman Disease, aiming to alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for patients. This aspect of care focuses on symptom management, which may include pain relief, fatigue management, and addressing other disease-related symptoms. Effective symptom control is achieved through a combination of medical treatments and lifestyle modifications.
Lifestyle modifications are an integral part of supportive care. Patients are often advised to adopt a healthy diet, engage in regular physical activity as tolerated, and practice stress management techniques. These changes can help strengthen the immune system, manage fatigue, and improve overall well-being.
Moreover, emotional and social support is crucial for patients coping with Castleman Disease. Support groups, either in-person or online, provide a platform for patients to share experiences and coping strategies. These groups can offer invaluable emotional support, helping patients feel less isolated and more empowered in their disease management journey.
However, managing Castleman Disease requires a well-coordinated, multidisciplinary approach. The comprehensive care team addresses the various aspects of the disease, while supportive care and lifestyle modifications play a significant role in improving patient outcomes and quality of life. This holistic approach is essential for the effective management of Castleman Disease.
Challenges in Treating Castleman Disease
Castleman Disease (CD), a rare and complex disorder of the lymph nodes and related tissues, presents significant challenges in treatment due to its unique characteristics and variability among patients. Understanding these challenges is crucial for healthcare providers and patients alike.
Variability and Diagnostic Complexity
One of the primary difficulties in treating CD stems from its variability. CD can manifest as either Unicentric Castleman Disease (UCD), which affects a single lymph node region, or Multicentric Castleman Disease (MCD), which impacts multiple lymph node areas and can have systemic symptoms. This variability complicates diagnosis, as the symptoms often mimic those of other diseases, such as lymphoma, making accurate and timely diagnosis challenging.
Treatment Response and Options
Once diagnosed, the treatment of CD varies widely. For UCD, surgical removal of the affected lymph node is often effective. However, MCD treatment is more complex, requiring a combination of therapies including immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and corticosteroids. The response to these treatments can be unpredictable, and what works for one patient may not be effective for another, necessitating a trial-and-error approach that can be frustrating for both patients and clinicians.
The Importance of Personalized Medicine
This variability underscores the importance of personalized medicine in the treatment of Castleman Disease. Personalized medicine involves tailoring treatment strategies to the individual characteristics of each patient, including their genetic profile, disease subtype, and response to previous treatments. This approach can help in identifying the most effective treatment with the least side effects for each patient.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Due to these complexities, ongoing research is critical. Scientists are continually exploring new treatments and therapeutic strategies, including targeted therapies that specifically address the molecular and genetic factors involved in CD. There is also a growing emphasis on patient-centric research, which focuses on understanding the unique experiences and needs of CD patients to improve quality of life and treatment outcomes.
However, treating Castleman Disease presents a range of challenges, from diagnosis to management. The key to effective treatment lies in personalized approaches tailored to the unique needs of each patient, supported by ongoing research and advancements in therapy. By acknowledging and addressing these challenges, healthcare providers can offer more effective and compassionate care to those battling this rare disease.
Conclusion:
As we conclude our comprehensive exploration of Castleman Disease treatment, it’s crucial to revisit the key points that make this journey both challenging and hopeful. Castleman Disease, a rare and complex condition, demands a multi-faceted treatment approach. The advancements in medical science have led to innovative treatments that significantly improve patient outcomes. These include targeted therapies, immunotherapy, and personalized medicine strategies that are tailored to the unique needs of each patient.
However, the battle against Castleman Disease is far from over. Continued research and development are essential to uncover new treatments and refine existing ones. The complexity of the disease means that every discovery opens new avenues for understanding and combating it more effectively.
Moreover, the role of patient support cannot be overstated. Living with Castleman Disease is a profound challenge, and patients require comprehensive care that addresses not just their physical symptoms but also their emotional and psychological well-being. Support groups, counseling, and patient education are integral components of the treatment process, empowering patients and their families to navigate this journey with resilience and hope.
In conclusion, while the road ahead is long and requires persistent effort, the progress made in treating Castleman Disease is a beacon of hope. It’s a call to the medical community, researchers, and patient support groups to continue their invaluable work. Together, through relentless research, innovative treatment approaches, and unwavering support for patients, we can look forward to a future where Castleman Disease is no longer a formidable foe but a condition that can be managed effectively and with greater understanding.