Carotid Artery Disease Treatment: Carotid artery disease, a significant medical condition, requires prompt attention due to its critical role in brain health.
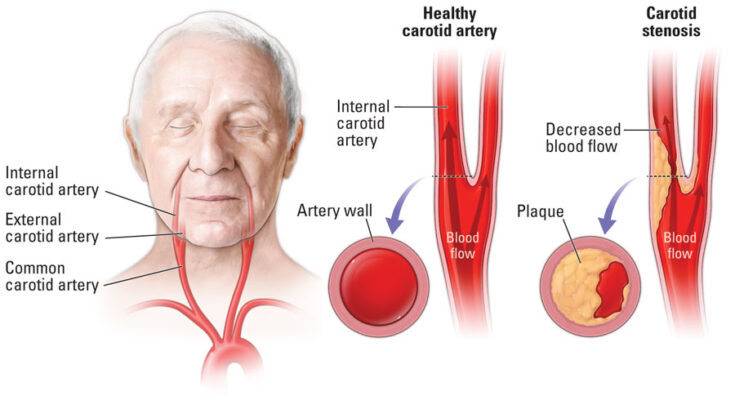
It occurs when the carotid arteries, the primary blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the brain, become narrowed or blocked, typically due to atherosclerosis.
Understanding the nuances of its diagnosis and treatment is essential for maintaining optimal brain function and preventing serious complications such as stroke.
What is Carotid Artery Disease?
Carotid artery disease is a significant medical condition where the carotid arteries, the main blood vessels that provide oxygen-rich blood to the brain, become narrowed. This narrowing is often due to a build-up of plaque – a combination of fat, cholesterol, and other substances in the bloodstream. The condition is a type of atherosclerosis and is a major cause of stroke, as it can significantly reduce blood flow to the brain or lead to the formation of blood clots.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of carotid artery disease:
- Age: The risk increases with age, particularly over 65 years.
- High Cholesterol: High levels of bad cholesterol (LDL) can contribute to plaque build-up.
- High Blood Pressure: This can damage artery walls and speed up plaque accumulation.
- Smoking: Tobacco use accelerates the hardening and narrowing of arteries.
- Diabetes: Poorly controlled diabetes increases the risk of atherosclerosis.
- Family History: A history of atherosclerosis or heart disease in the family can increase risk.
- Obesity: Excess weight is a contributing factor to carotid artery disease.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of regular exercise can worsen other risk factors.
Statistics and Prevalence
Carotid artery disease is a prevalent condition, especially among older adults. According to recent studies:
- Approximately 0.5% of adults aged 40 to 59, and up to 10% of adults over 80 years, have significant narrowing of the carotid arteries.
- Men are more likely than women to develop carotid artery disease, although the risk for women increases after menopause.
Impact on Health and Quality of Life
The implications of carotid artery disease on health and quality of life are substantial:
- Stroke Risk: It’s a leading cause of stroke, which can result in significant disability or death.
- Cognitive Impairment: Reduced blood flow to the brain can affect cognitive functions.
- Physical Limitations: Stroke or mini-strokes (transient ischemic attacks) can lead to physical disabilities.
- Emotional Impact: There is an increased risk of depression and anxiety due to the potential severe outcomes of the disease.
Early diagnosis and management of risk factors are crucial in preventing the progression of carotid artery disease. Regular check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and medication (if prescribed) play pivotal roles in managing this condition.
Common Symptoms of Carotid Artery Disease
Carotid artery disease, a condition where the arteries in your neck become narrowed or blocked, can lead to serious health complications. Recognizing its symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Sudden Weakness or Numbness: This often occurs on one side of the body, including the face, arm, or leg.
- Difficulty Speaking or Understanding Speech: Experiencing confusion or trouble forming words can be a telltale sign.
- Vision Problems: Sudden blurred vision or loss of vision in one or both eyes.
- Dizziness or Loss of Balance: Feeling unsteady or having trouble with coordination.
- Severe Headache: An abrupt, intense headache without any known cause.
Warning Signs That Warrant Medical Attention
Certain symptoms of carotid artery disease are warning signs that require immediate medical attention:
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA): Often called a mini-stroke, it includes temporary symptoms similar to a stroke, such as weakness, numbness, or speech problems.
- Stroke: If you experience any stroke symptoms, it’s critical to seek emergency care. These include sudden numbness, confusion, trouble walking, severe headache, and more.
The Role of Awareness in Early Diagnosis
Awareness of these symptoms plays a vital role in the early diagnosis of carotid artery disease. Early diagnosis can significantly reduce the risk of severe outcomes like stroke. Paying attention to your body and seeking medical advice when experiencing any unusual symptoms can be lifesaving. Regular check-ups and discussions with your doctor about any risk factors you may have, such as high blood pressure, smoking, or a family history of cardiovascular disease, are also important in early detection.
However, being informed about the symptoms and early signs of carotid artery disease is crucial. Timely medical intervention can lead to a better prognosis and prevent serious complications. Remember, your health is in your hands, and staying vigilant about changes in your body is key.
Diagnostic Procedures of Carotid Artery Disease
Understanding the various diagnostic procedures for this condition is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the diagnostic methods for carotid artery disease, emphasizing the importance of a thorough approach in treatment planning.
Physical Examination and Medical History Analysis
The initial step in diagnosing carotid artery disease involves a physical examination and an in-depth analysis of the patient’s medical history. Healthcare providers will look for symptoms such as a bruit, an abnormal sound heard over the carotid artery with a stethoscope, indicating turbulent blood flow. Additionally, a detailed discussion of the patient’s personal and family medical history, including factors like high cholesterol, hypertension, and smoking habits, provides insights into the risk of carotid artery disease.
Non-Invasive Tests
Following the preliminary examination, non-invasive tests are often employed. These include:
- Carotid Ultrasound (Duplex Ultrasound): This common test uses sound waves to create images of the internal structure of the carotid arteries, revealing plaque buildup, blockages, and blood flow irregularities.
- Computerized Tomography Angiography (CTA): CTA combines a CT scan with an injection of contrast material to produce detailed images of the carotid arteries and highlight any obstructions or narrowing.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA): Similar to CTA, MRA uses magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of the carotid arteries without the need for contrast dye.
These non-invasive tests are crucial as they provide valuable information about the condition of the carotid arteries without the risks associated with invasive procedures.
Invasive Tests
In certain cases, more invasive tests may be necessary, such as:
- Carotid Angiography: This procedure involves inserting a catheter into a blood vessel in the arm or leg and guiding it to the carotid arteries. A contrast dye is injected, and X-rays are taken to visualize the arteries’ interior.
While invasive, carotid angiography is considered the gold standard for evaluating carotid artery disease. It provides detailed information about the extent and severity of the disease.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis in Treatment Planning
Accurate diagnosis of carotid artery disease is paramount for several reasons:
- Determining the Severity: Understanding the extent of the disease helps in deciding the urgency and type of treatment required.
- Customizing Treatment Plans: Treatment for carotid artery disease varies from lifestyle changes and medications to surgical procedures like carotid endarterectomy or stenting. A precise diagnosis ensures the selection of the most appropriate treatment for each individual.
- Preventing Complications: Accurate diagnosis helps in preventing serious complications like strokes, as it enables timely and appropriate intervention.
However, the diagnosis of carotid artery disease involves a blend of physical examinations, medical history analysis, non-invasive and invasive tests. Each plays a vital role in ensuring an accurate diagnosis, which is crucial for effective treatment planning and the prevention of serious complications. As medical technology advances, these diagnostic procedures continue to evolve, offering more precision and safety in the management of carotid artery disease.
Treatment Options for Carotid Artery Disease
Understanding the various treatment options available is crucial for those diagnosed with this condition. The choice of treatment largely depends on the severity of the disease, symptoms, and overall health of the patient.
Lifestyle Changes and Medication
For early stages or mild forms of carotid artery disease, lifestyle modifications coupled with medication can be highly effective. These include:
- Adopting a Heart-Healthy Diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help manage cholesterol levels and reduce artery-clogging plaque buildup.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, can improve overall cardiovascular health.
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking cessation is critical as it is a major risk factor for the development and progression of carotid artery disease.
- Managing Chronic Conditions: Keeping conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol under control is vital.
Medications may be prescribed to lower cholesterol levels, manage high blood pressure, and reduce the risk of blood clots.
Surgical Treatments
In more advanced cases, surgical interventions may be necessary. These include:
- Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA): This is a traditional surgical procedure where the surgeon removes plaque from the carotid artery. It’s typically recommended for patients with significant blockage (usually 50% or more).
- Carotid Artery Bypass: In this procedure, a graft is used to create a new pathway for blood flow around the blocked area of the carotid artery.
Minimally Invasive Treatments
Minimally invasive options offer alternatives to traditional surgery and include:
- Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting: This procedure involves temporarily inserting and inflating a tiny balloon where the carotid artery is clogged to widen the artery. A stent, a small metal or plastic tube, is then placed to keep the artery open.
When Are These Treatments Recommended?
- Lifestyle Changes and Medication: Recommended for all patients, particularly those with mild to moderate carotid artery disease.
- Surgical Treatments: Often advised for patients with severe narrowing or blockage, especially if they have had stroke symptoms.
- Minimally Invasive Treatments: Typically considered for patients who are high-risk candidates for traditional surgery due to other medical conditions, or for those with recurrent stenosis.
However, the treatment of carotid artery disease is multifaceted, often starting with lifestyle changes and medication. As the condition progresses, more invasive treatments like surgery or minimally invasive procedures may be necessary. The choice of treatment depends on the individual’s specific condition, medical history, and overall health. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Advances in Carotid Artery Disease Treatment
Overview of Recent Advancements and Research
Recent years have witnessed significant progress in the treatment of Carotid Artery Disease (CAD), a condition that significantly increases the risk of stroke. Advancements in medical research and technology have led to more effective and safer treatments. Pioneering studies have focused on understanding the underlying causes of CAD, leading to developments in both medication and surgical techniques. Innovative imaging technologies have improved the diagnosis and monitoring of the disease, enabling more personalized and timely interventions.
Emerging Treatments and Technologies
One of the most exciting areas in CAD treatment is the emergence of new, minimally invasive procedures. For instance, advancements in endovascular surgery, such as Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS) and TransCarotid Artery Revascularization (TCAR), have shown promising results. These procedures involve less trauma and quicker recovery times compared to traditional surgeries. Moreover, the development of new medications that target the specific pathways involved in artery blockage is revolutionizing patient care. These pharmaceuticals aim to reduce the progression of the disease and prevent stroke more effectively than ever before.
Future Prospects in Treatment Options
Looking to the future, the prospects for CAD treatment are increasingly optimistic. Research is delving into the potential of gene therapy and regenerative medicine, aiming to repair or regenerate the damaged arterial walls. Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning are expected to enhance diagnostic accuracy and predict treatment outcomes, leading to more customized treatment plans. Furthermore, ongoing clinical trials are continuously evaluating the safety and efficacy of new treatments, setting the stage for groundbreaking therapies in the years to come.
However, the landscape of Carotid Artery Disease treatment is rapidly evolving, marked by significant research advancements, emerging technologies, and promising future prospects. These developments not only offer hope for improved patient outcomes but also pave the way for more innovative approaches in the management and treatment of CAD.
Living with Carotid Artery Disease
Living with Carotid Artery Disease (CAD) necessitates adopting a healthier lifestyle to manage and potentially improve the condition. Lifestyle changes are pivotal in slowing the progression of the disease and reducing the risk of complications like strokes.
- Healthy Eating Habits: Adopt a diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol. Focus on consuming more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. This approach aids in maintaining a healthy weight and reduces the buildup of plaque in the arteries.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, can enhance cardiovascular health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Always consult your doctor before starting any new exercise regimen.
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for CAD. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of further complications and improve overall vascular health.
- Limiting Alcohol Intake: Excessive alcohol consumption can elevate blood pressure. Limiting alcohol intake can help in maintaining a healthy blood pressure level.
Importance of Regular Check-Ups and Monitoring
Regular medical check-ups are crucial for individuals with Carotid Artery Disease. These include:
- Monitoring Blood Pressure: High blood pressure can accelerate arterial damage. Regular monitoring helps in managing blood pressure effectively.
- Cholesterol Level Checks: High cholesterol levels can lead to plaque buildup. Regular lipid profile tests are important to keep cholesterol levels in check.
- Ultrasound Scans: Periodic ultrasound scans of the carotid arteries can help monitor the condition and assess the effectiveness of lifestyle changes and medications.
Support Systems and Resources
Dealing with CAD can be challenging, but you’re not alone. Leverage support systems and resources:
- Support Groups: Joining a support group for people with CAD can provide emotional support and practical advice from others who are going through similar experiences.
- Educational Resources: Educate yourself about CAD through reliable sources such as healthcare providers, medical websites, and patient education materials.
- Professional Counseling: If you’re struggling with anxiety or depression related to your condition, consider seeking professional counseling.
Living with Carotid Artery Disease requires a proactive approach to health and well-being. By making lifestyle modifications, staying vigilant with regular check-ups, and utilizing available support systems, individuals with CAD can lead a healthier and more fulfilling life.
FAQs: Understanding Carotid Artery Disease and Its Treatment
What is Carotid Artery Disease?
Carotid artery disease occurs when the carotid arteries, the main blood vessels that provide blood to the brain, become narrowed or blocked. This blockage is usually caused by a buildup of plaque, a combination of fat, cholesterol, and other substances.
What are the Symptoms of Carotid Artery Disease?
In many cases, carotid artery disease doesn’t produce noticeable symptoms until it severely narrows or blocks a carotid artery. Signs and symptoms may include a sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arms, or legs, typically on one side of the body, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, dizziness or loss of balance, and sudden, severe headaches with no known cause.
How is Carotid Artery Disease Diagnosed?
Carotid artery disease is often discovered during a routine examination. Your doctor may hear an abnormal sound, called a bruit, over the artery when using a stethoscope. Other diagnostic tests include carotid ultrasound, computerized tomography (CT) scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or angiography.
What are the Treatment Options for Carotid Artery Disease?
Treatment for carotid artery disease usually involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and possibly surgery. Lifestyle changes can include quitting smoking, eating a heart-healthy diet, and exercising regularly. Medications may be prescribed to lower blood pressure or cholesterol levels, and prevent blood clots. In severe cases, surgical procedures such as carotid endarterectomy or carotid artery angioplasty with stenting may be necessary.
Can Carotid Artery Disease be Prevented?
While not all factors of carotid artery disease can be controlled, certain lifestyle changes can significantly reduce risk. These include maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, avoiding smoking, controlling blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and diabetes.
Is Carotid Artery Disease Reversible?
Once plaque builds up in the carotid arteries, it’s generally there to stay. However, with lifestyle changes and treatment, the progression of the disease can be slowed down and the risk of stroke reduced.
Should I See a Doctor for Carotid Artery Disease?
If you have risk factors for carotid artery disease, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, tobacco use, or a family history of the disease, it’s important to discuss with your doctor whether you need to be screened. If you experience any symptoms of a stroke, seek immediate medical attention.
Conclusion
Treatment strategies for carotid artery disease range from lifestyle modifications and medications to surgical interventions like carotid endarterectomy or stenting. The choice of treatment depends on the disease’s progression and the patient’s overall health status.
Emphasizing the importance of professional medical advice cannot be overstated. If you suspect you or a loved one is at risk or showing symptoms of carotid artery disease, consulting with healthcare professionals is imperative. They can offer personalized guidance and an appropriate treatment plan based on individual health needs and risks.
Lastly, awareness and timely treatment of carotid artery disease cannot be ignored. Recognizing the early signs and seeking prompt medical care can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications like stroke. Staying informed about this condition and maintaining regular health check-ups are key steps in ensuring a healthy cardiovascular system. Remember, proactive and informed healthcare decisions can lead to better health outcomes and quality of life.